Can I Get Equity From a Private Equity Backed Company
What is Private Company Valuation?
Private company valuation Valuation Methods When valuing a company as a going concern there are three main valuation methods used: DCF analysis, comparable companies, and precedent transactions is the set of procedures used to appraise a company's current net worth. For public companies, this is relatively straightforward: we can simply retrieve the company's stock Stock What is a stock? An individual who owns stock in a company is called a shareholder and is eligible to claim part of the company's residual assets and earnings (should the company ever be dissolved). The terms "stock", "shares", and "equity" are used interchangeably. price and the number of shares outstanding from databases such as Google Finance. The value of the public company, also called market capitalization, is the product of the said two values.
Such an approach, however, will not work with private companies, since information regarding their stock value is not publicly listed. Moreover, as privately held firms often are not required to operate by the stringent accounting and reporting standards that govern public firms, their financial statements may be inconsistent and unstandardized, and as such, are more difficult to interpret.
Here, we will introduce three common methods for valuing private companies, using data available to the public.
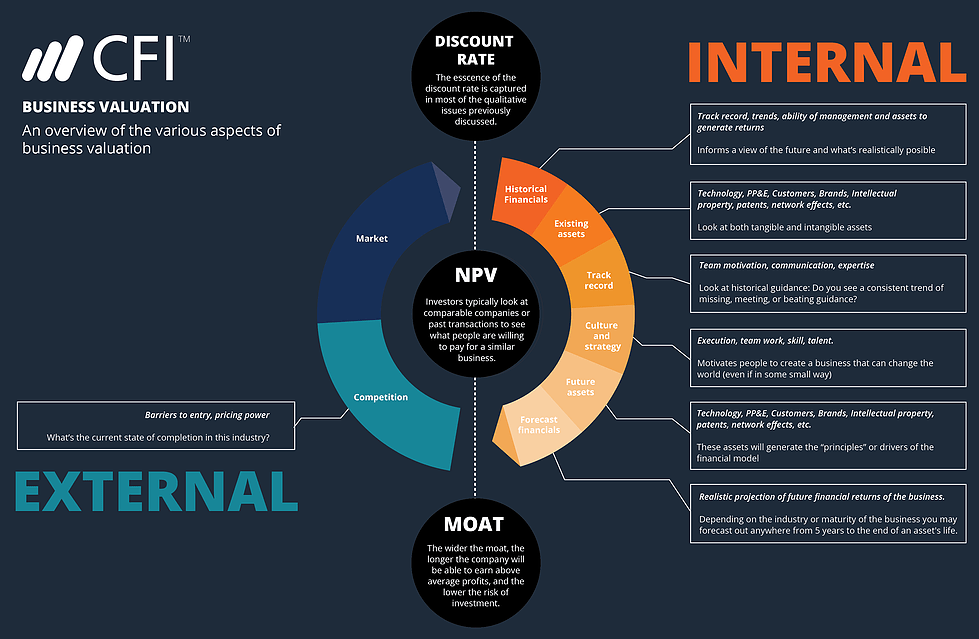
To learn more, read about our business valuation infographic DCF Analysis Infographic How discounted cash flow (DCF) really works. This DCF analysis infographic walks through the various steps involved in building a DCF model in Excel. .
Common Methods for Valuing Private Companies
#1 Comparable Company Analysis (CCA)
The Comparable Company Analysis Comparable Company Analysis This guide shows you step-by-step how to build comparable company analysis ("Comps") and includes a free template and many examples. (CCA) method operates under the assumption that similar firms in the same industry have similar multiples Types of Valuation Multiples There are many types of valuation multiples used in financial analysis. They can be categorized as equity multiples and enterprise value multiples. . When the financial information of the private company is not publicly available, we search for companies that are similar to our target valuation and determine the value of the target firm using the comparable firms' multiples. This is the most common private company valuation method.
To apply this method, we first identify the target firm's characteristics in size, industry, operation, etc., and establish a "peer group" of companies that share similar characteristics. We then collect the multiples of these companies and calculate the industry average. While the choices of multiples can depend on the industry and growth stage of firms, we hereby provide an example of valuation using the EBITDA multiple EBITDA Multiple The EBITDA multiple is a financial ratio that compares a company's Enterprise Value to its annual EBITDA. This multiple is used to determine the value of a company and compare it to the value of other, similar businesses. A company's EBITDA multiple provides a normalized ratio for differences in capital structure, , as it is one of the most commonly used multiples.
The EBITDA EBITDA EBITDA or Earnings Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation, Amortization is a company's profits before any of these net deductions are made. EBITDA focuses on the operating decisions of a business because it looks at the business' profitability from core operations before the impact of capital structure. Formula, examples is a firm's net income adjusted for interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization, and can be used as an approximate representation of said firm's free cash flow. The firm's valuation formula is expressed as follows:
Value of target firm = Multiple (M) x EBITDA of the target firm
Where, the Multiple (M) is the average of Enterprise Value Enterprise Value (EV) Enterprise Value, or Firm Value, is the entire value of a firm equal to its equity value, plus net debt, plus any minority interest /EBITDA of comparable firms, and the EBITDA of the target firm is typically projected for the next twelve months.
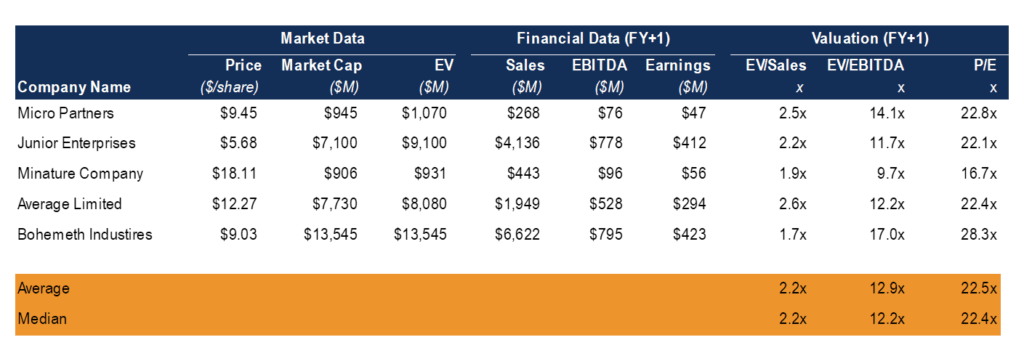
The image shown above is a Comps Table from CFI's Business Valuation Course.
#2 Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) method
The Discounted Cash Flow DCF Model Training Free Guide A DCF model is a specific type of financial model used to value a business. The model is simply a forecast of a company's unlevered free cash flow (DCF) method takes the CCA method one-step further. As with the CCA method, we estimate the target's discounted cash flow estimations, based on acquired financial information from its publicly-traded peers.
Under the DCF method, we start by determining the applicable revenue growth rate for the target firm. This is achieved by calculating the average growth rates of the comparable firms. We then make projections of the firm's revenue, operating expenses, taxes, etc., and generate free cash flows Free Cash Flow (FCF) Free Cash Flow (FCF) measures a company's ability to produce what investors care most about: cash that's available be distributed in a discretionary way. (FCF) of the target firm, typically for 5 years. The formula of free cash flow is given as:
Free cash flow = EBIT (1-tax rate) + (depreciation Depreciation Expense When a long-term asset is purchased, it should be capitalized instead of being expensed in the accounting period it is purchased in. ) + (amortization) – (change in net working capital Net Working Capital Net Working Capital (NWC) is the difference between a company's current assets (net of cash) and current liabilities (net of debt) on its balance sheet. ) – (capital expenditure)
We usually use the firm's weighted average cost of capital (WACC) WACC WACC is a firm's Weighted Average Cost of Capital and represents its blended cost of capital including equity and debt. as the appropriate discount rate. To derive a firm's WACC, we need to know its cost of equity, cost of debt, tax rate, and capital structure. Cost of equity is calculated using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) is a model that describes the relationship between expected return and risk of a security. CAPM formula shows the return of a security is equal to the risk-free return plus a risk premium, based on the beta of that security . We estimate the firm's beta by taking the industry average beta. Cost of debt is dependent on the target's credit profile, which affects the interest rate at which it incurs debt.
We also refer to the target's public peers to find the industry norm of tax rate and capital structure. Once we have the weights of debt and equity, cost of debt, and cost of equity, we can derive the WACC.
With all the above steps completed, the valuation of the target firm can be calculated as:
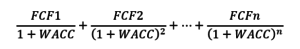
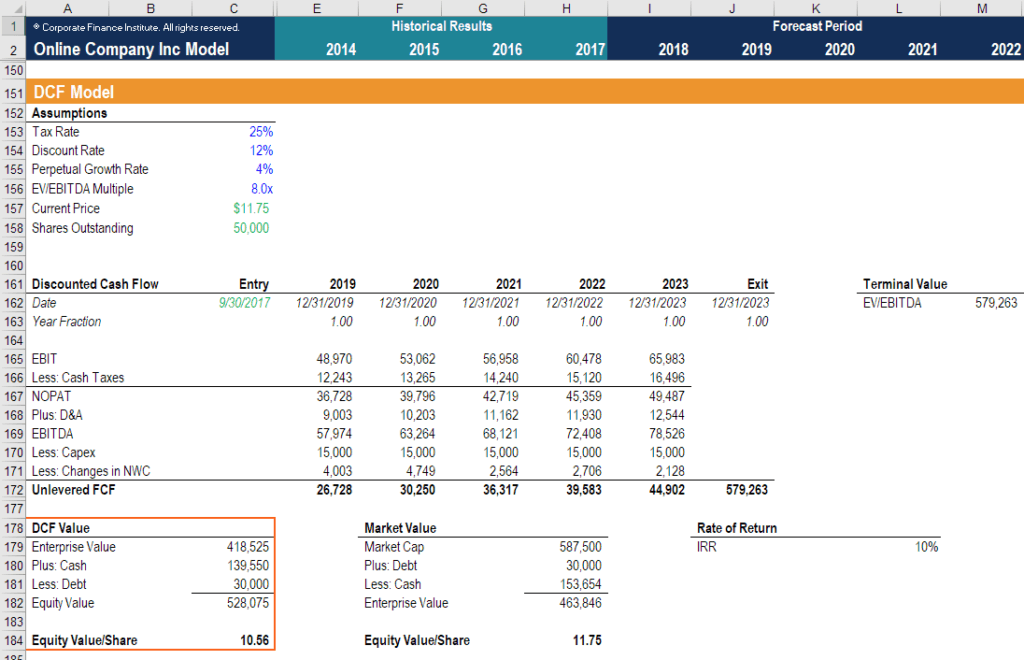
It should be noted that performing a DCF analysis requires significant financial modeling What is Financial Modeling Financial modeling is performed in Excel to forecast a company's financial performance. Overview of what is financial modeling, how & why to build a model. experience. The best way to learn financial modeling is through practice and direct instruction from a professional. CFI's financial modeling course is one of the easiest ways to learn this skill.
Launch CFI financial modeling courses now!
#3 First Chicago Method
The First Chicago Method is a combination of the multiple-based valuation method and the discounted cash flow method. The distinct feature of this method lies in its consideration of various scenarios of the target firm's payoffs. Usually, this method involves the construction of three scenarios: a best-case (as stated in the firm's business plan), a base-case (the most likely scenario), and a worst-case scenario. A probability is assigned to each case.
We apply the same approach in the first two methods to project case-specific cash flows and growth rates for several years (typically a five-year forecast period). We also project the terminal value of the firm using the Gordon Growth Model Gordon Growth Model The Gordon Growth Model – also known as the Gordon Dividend Model or dividend discount model – is a stock valuation method that calculates a stock's intrinsic value, regardless of current market conditions. Investors can then compare companies against other industries using this simplified model . Subsequently, the valuation of each case is derived using the DCF method. Finally, we arrive at the valuation of the target firm by taking the probability-weighted average of the three scenarios.
This private company valuation method can be used by venture capitalists and private equity Private Equity Career Profile Private equity analysts & associates perform similar work as in investment banking. The job includes financial modeling, valuation, long hours & high pay. Private equity (PE) is a common career progression for investment bankers (IB). Analysts in IB often dream of "graduating" to the buy side, investors as it provides a valuation that incorporates both the firm's upside potential and downside risk.
Limitation and Application in the Real World
As we can see, private company valuation is primarily constructed from assumptions and estimations. While taking the industry average on multiples and growth rates provides a decent guess for the true value of the target firm, it cannot account for extreme one-time events that affected the comparable public firm's value. As such, we need to adjust for a more reliable rate, excluding the effects of such rare events.
Additionally, recent transactions in the industry such as acquisitions, mergers Mergers Acquisitions M&A Process This guide takes you through all the steps in the M&A process. Learn how mergers and acquisitions and deals are completed. In this guide, we'll outline the acquisition process from start to finish, the various types of acquirers (strategic vs. financial buys), the importance of synergies, and transaction costs , or IPOs can provide us with financial information that gives a far more sophisticated estimate of the target firm's worth.
Learn More!
We hope this has been a helpful guide to private company valuation. To keep learning more about how to value a business, we highly recommend these additional resources below:
- Valuation Methods Valuation Methods When valuing a company as a going concern there are three main valuation methods used: DCF analysis, comparable companies, and precedent transactions
- Valuation Career Profile Valuations Analyst Career Profile A valuations analyst provides valuation services for public and private companies. They typically focus on the identification and valuation of intangible assets and, more specifically, with goodwill impairment and purchase price allocation (PPA). A career as an analyst on the valuation team can require significant financial modeling and analysis.
- EBITDA Multiple EBITDA Multiple The EBITDA multiple is a financial ratio that compares a company's Enterprise Value to its annual EBITDA. This multiple is used to determine the value of a company and compare it to the value of other, similar businesses. A company's EBITDA multiple provides a normalized ratio for differences in capital structure,
- Multiple Analysis Multiples Analysis The multiples analysis is a valuation technique that utilizes different financial metrics from comparable companies to value a target company.
- Types of Multiples Types of Valuation Multiples There are many types of valuation multiples used in financial analysis. They can be categorized as equity multiples and enterprise value multiples.
Can I Get Equity From a Private Equity Backed Company
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/valuation/private-company-valuation/
0 Response to "Can I Get Equity From a Private Equity Backed Company"
Post a Comment